Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA)
Content of This Page
1- Definition and Key Features
2- Epidemiology and Risk Factors
3-Immunopathogenesis of RA
4- Clinical Features of RA
5– Classification Criteria (2010 ACR/EULAR)
6- Laboratory Findings
7- Laboratory Findings
8- Radiological Features
9- Disease Activity Monitoring
10- Treatment Goals and Strategy
11- Non-Pharmacological Management
12- Prognosis and Predictors of Poor Outcome
13- RA vs. Other Arthritis
14- Complications of RA
15- Felty Syndrome
Definition and Key Features
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune inflammatory disorder that:
Primarily targets synovial joints, leading to progressive joint destruction, deformity, and disability.
Is characterized by symmetrical polyarthritis, especially of the small joints (PIP, MCP, wrists, MTP).
Often includes extra-articular manifestations involving the lungs, heart, eyes, skin, and blood.
-It is a relapsing–remitting or progressive condition, with varying severity across individuals.
Key Features of RA:
Chronic: Persists >6 weeks (used in diagnostic criteria)
Symmetric: Affects both sides of the body equally
Inflammatory: Prolonged morning stiffness, warm/swollen joints
Autoimmune: Presence of autoantibodies (RF and/or ACPA)
Systemic: Can involve skin, lungs, cardiovascular system, and blood
–Mnemonic: “4S” = Synovial, Symmetric, Systemic, Seropositive (often)
Epidemiology and Risk Factors
Affects ~1% of the population.
Female:male ratio ≈ 3:1.
Peak onset: 40–60 years.
Risk factors: HLA-DRB1, smoking, silica exposure, periodontal disease.
Immunopathogenesis
Initiation by autoreactive T cells and B cells.
Cytokines involved: TNF-α, IL-1, IL-6 → drive inflammation and joint damage.
Chronic inflammation causes synovial hyperplasia (pannus) and erosive joint destruction.
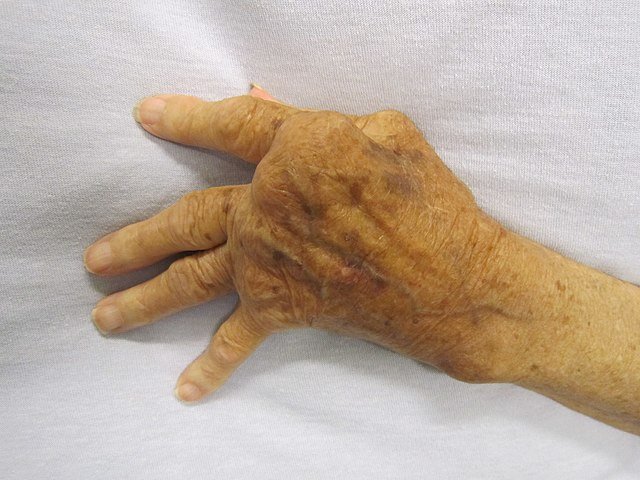
Clinical Features
Articular:
Symmetric small joint arthritis (PIP, MCP, wrists, MTPs).
Morning stiffness > 30 minutes, improves with use.
Progresses to joint deformities: ulnar deviation, swan neck, boutonnière.
Extra-articular (esp. if RF/ACPA+):
Rheumatoid nodules
Lung: ILD, pleural effusion
Heart: pericarditis, ↑ CVD
Eye: episcleritis, keratoconjunctivitis sicca
Felty syndrome: RA + splenomegaly + neutropenia
Classification Criteria (2010 ACR/EULAR)
Diagnosis requires a score ≥6/10 from four domains:
Joint involvement
Serology (RF, ACPA)
Acute-phase reactants (CRP/ESR)
Duration >6 weeks
-Used for early diagnosis before radiologic changes.
Laboratory Findings
Rheumatoid Factor (RF): Positive in ~70% (not specific)
Anti-CCP (ACPA): More specific, predicts erosive disease
↑ ESR/CRP, anaemia of chronic disease
May see leukopenia in Felty syndrome
Radiological Features
Early: Soft tissue swelling, juxta-articular osteopenia
Late: Joint space narrowing, marginal erosions (esp. MCP, PIP)
MRI/Ultrasound: detect early synovitis and bone edema
Disease Activity Monitoring
Use DAS28 (Disease Activity Score in 28 joints):
Includes joint count, ESR/CRP, and patient global score
Guides escalation or tapering of therapy
Treatment Goals and Strategy (Treat-to-Target)
Aim: Achieve remission or low disease activity
Stepwise approach:
Start DMARDs early (methotrexate = gold standard)
Add biologic (e.g. TNF inhibitor) if poor response
Consider JAK inhibitors if unresponsive to biologics
Use short-term steroids as bridge therapy
Non-Pharmacological Management
Exercise and joint protection
Smoking cessation
Vaccination (pneumococcus, influenza, avoid live vaccines if immunosuppressed)
Cardiovascular risk assessment
Prognosis and Predictors of Poor Outcome
Worse prognosis with:
High RF/ACPA titres
Early erosions on X-ray
Extra-articular features
High initial disease activity
RA vs. Other Arthritis
| Feature | RA | Osteoarthritis | Psoriatic Arthritis |
|---|---|---|---|
| Onset | Insidious | Gradual | Variable |
| Joint pattern | Symmetric, small joints | Asymmetric, weight-bearing | Asymmetric, DIP, spine |
| Morning stiffness | >30 min | <30 min | >30 min |
| RF/ACPA | + | – | – |
| Nodules | Yes | No | Possible (enthesitis) |
Complications
Joint deformity and disability
Osteoporosis (from disease or steroids)
Cardiovascular disease
Amyloidosis
Infection risk (immunosuppressants)
Felty Syndrome
Triad: RA + splenomegaly + neutropenia
↑ Risk of infections
Associated with seropositive, long-standing RA