Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID)
Content of This Page
1- Introduction
2- Causes
3- Symptoms
4- Stages of The Disease
5- Treatment
6- What Should You Avoid
Introduction
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease (PID) is an infection of the female reproductive organs, including the uterus, fallopian tubes, and ovaries. It is often caused by sexually transmitted infections (STIs) like chlamydia or gonorrhea, but can also result from other infections or procedures. PID can lead to pain, fever, abnormal vaginal discharge, and, if untreated, can cause serious complications such as infertility or chronic pelvic pain.

Causes
- Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs): Chlamydia, gonorrhea
- Bacterial Infections: Other bacteria beyond STIs
- Post-Surgical Infections: After procedures like childbirth, abortion, or pelvic surgery
- Intrauterine Devices (IUDs): Rarely, IUDs can introduce bacteria
- Multiple Sexual Partners: Increases risk of STIs
- Unprotected Sex: Increases risk of STIs and subsequent PID
Symptoms
- Pelvic pain or lower abdominal pain
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Fever or chills
- Painful intercourse
- Painful urination
- Irregular menstrual bleeding
- Nausea or vomiting
- Lower back pain
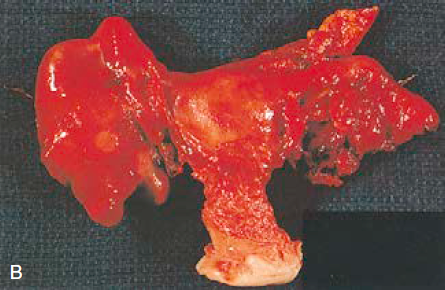
Stages of The Disease
Acute PID
- Sudden onset of symptoms with severe pain, fever, and other signs of infection.
Chronic PID
- Persistent symptoms or recurrent infections leading to long-term pelvic pain and potential complications.
Severe PID
- Advanced PID with complications such as abscesses, scarring, or damage to reproductive organs, potentially leading to infertility or chronic pain.
Treatment
- Antibiotics: To treat the underlying infection, often a combination of drugs to cover various bacteria.
- Pain Relievers: NSAIDs or other medications to manage pain and discomfort.
- Hospitalization: For severe cases or if oral antibiotics are not effective; may include intravenous antibiotics and monitoring.
- Treatment of Sexual Partners: To prevent reinfection and spread of STIs.
- Surgery: In cases of abscesses or severe complications, surgical intervention may be needed.
What Should You Avoid
- Unprotected sex
- Multiple sexual partners
- Delayed treatment of STIs
- Poor personal hygiene
- Smoking
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Self-medicating without medical guidance