Leukemia
Content of This Page
1- Introduction
2- Causes
3- Symptoms
4- Stages of The Disease
5- Treatment
6- What Should You Avoid
Introduction
Leukemia is a cancer that starts in the blood-forming tissues of the body, primarily the bone marrow, and leads to the production of abnormal white blood cells. These cancerous cells can multiply uncontrollably and interfere with the production of normal blood cells, causing issues like frequent infections, anemia, and bleeding problems.
Causes
Genetic Mutations:
- Abnormalities in the DNA of blood cells can lead to leukemia.
Genetic Disorders:
- Conditions like Down syndrome and other genetic disorders can increase the risk.
Exposure to Radiation:
- High levels of radiation, such as from cancer treatments or nuclear accidents, can raise the risk.
Chemotherapy:
- Certain chemotherapy drugs used to treat other cancers may increase the risk of leukemia later.
Exposure to Chemicals:
- Prolonged exposure to certain chemicals, like benzene, is associated with a higher risk.
Family History:
- Having a close relative with leukemia may slightly increase the risk, suggesting a genetic component.
Immune System Disorders:
- Conditions that affect the immune system may be linked to a higher risk of leukemia.
Symptoms
- Fatigue and Weakness
- Frequent Infections
- Unexplained Bruising or Bleeding
- Pale or Sallow Skin
- Swollen Lymph Nodes
- Unexplained Weight Loss
- Fever or Chills
- Bone or Joint Pain
- Night Sweats
- Shortness of Breath
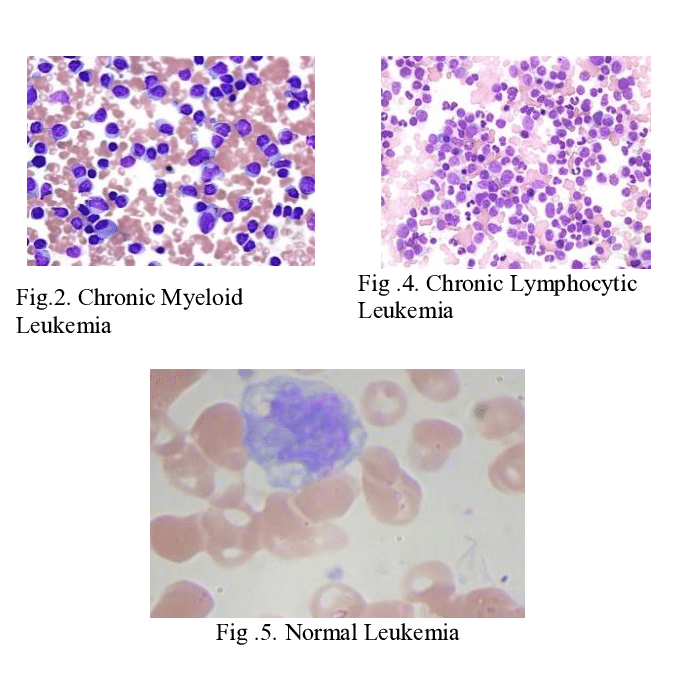
Stages of The Disease
Acute Leukemia:
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL): Rapid progression with high levels of immature white blood cells.
- Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML): Rapid progression with abnormal white blood cells that are not fully developed.
Chronic Leukemia:
- Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL): Slow progression with mature but dysfunctional lymphocytes.
- Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML): Slow progression with an accumulation of mature but abnormal myeloid cells.
Refractory Leukemia:
- Resistant to Initial Treatment: Leukemia that does not respond to standard treatments.
Relapsed Leukemia:
- Recurrence After Treatment: Leukemia returns after initial treatment and remission.
Treatment
Chemotherapy:
- Primary Treatment: Uses drugs to kill leukemia cells or stop their growth.
Radiation Therapy:
- Targeted Treatment: Uses high-energy rays to target and destroy leukemia cells, often used for specific areas like the brain or lymph nodes.
Targeted Therapy:
- Specific Drugs: Targets specific molecules involved in leukemia cell growth and survival.
Immunotherapy:
- Boosts the Immune System: Uses drugs or treatments to help the immune system recognize and attack leukemia cells.
Stem Cell Transplant (Bone Marrow Transplant):
- Replaces Damaged Bone Marrow: Involves infusing healthy stem cells to replace the diseased bone marrow.
Supportive Care:
- Manages Symptoms: Includes medications, transfusions, and treatments to manage side effects and complications.
Clinical Trials:
- Experimental Treatments: Provides access to new therapies and advances in treatment
What Should You Avoid
Infections:
- Avoid Exposure: Minimize contact with people who are sick or have infections due to a weakened immune system.
Certain Medications:
- Over-the-Counter Drugs: Avoid medications like aspirin or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) unless prescribed by your doctor.
Raw or Undercooked Foods:
- Food Safety: Avoid foods that can pose infection risks, such as raw meat, seafood, or eggs.
High-Risk Activities:
- Injury Risk: Avoid activities or sports that could lead to injury or bleeding.
Unnecessary Procedures:
- Invasive Procedures: Avoid unnecessary surgeries or dental work without proper precautions and consultation with your healthcare provider.
Exposure to Chemicals:
- Toxic Substances: Avoid exposure to harmful chemicals or toxins that may impact overall health.
Ignoring Symptoms:
- Seek Medical Advice: Don’t ignore new or worsening symptoms; report them to your healthcare provider promptly.
Smoking and Alcohol:
- Avoid These: Both can interfere with treatment and recovery.