Fungal Infections
Content of This Page
1- Introduction
2- Causes
3- Symptoms
4- Stages of The Disease
5- Treatment
6- What Should You Avoid
Introduction
Fungal infections occur when fungi invade and grow on the skin, nails, or mucous membranes. They can cause symptoms like itching, redness, and scaling. Common fungal infections include athlete’s foot, ringworm, and yeast infections.
Causes
- Direct Contact: Touching contaminated surfaces or infected individuals.
- Warm, Moist Environments: Fungi thrive in warm, damp places, such as locker rooms or sweaty shoes.
- Compromised Immune System: Conditions or medications that weaken the immune system.
- Poor Hygiene: Inadequate personal hygiene practices can increase the risk of infection.
- Skin Trauma: Cuts or abrasions can provide entry points for fungi.
- Shared Personal Items: Using items like towels or shoes that are contaminated.
- Chronic Health Conditions: Conditions like diabetes or HIV can increase susceptibility to infections.
Symptoms
- Itching: Persistent itching at the site of infection.
- Redness: Inflamed, reddish areas on the skin.
- Scaling or Peeling: Dry, flaky skin or nail surfaces.
- Rash: Rash that may be ring-shaped or with defined edges.
- Swelling: Localized swelling in the affected area.
- Blisters or Pustules: Fluid-filled blisters or pustules in some cases.
- Discoloration: Changes in color of the skin or nails, such as darkening or yellowing.
- Cracking or Fissures: Skin may crack or develop fissures, particularly in fungal infections of the feet.
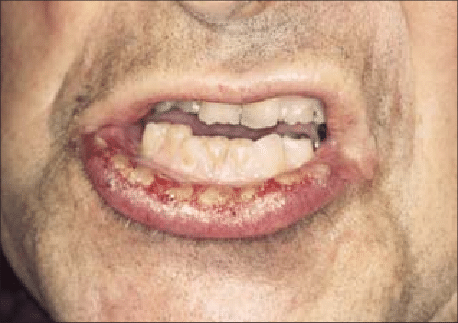
Stages of The Disease
Initial Infection:
- Symptoms: Mild itching, redness, and irritation. The affected area may start to show signs of fungal growth.
- Description: Fungi begin to colonize and infect the surface of the skin or nails.
Early Stage:
- Symptoms: Increased itching, redness, and scaling. The infection may spread slowly and develop visible rashes or lesions.
- Description: The infection becomes more apparent, with symptoms becoming more pronounced and potentially spreading to nearby areas.
Advanced Stage:
- Symptoms: Severe itching, intense redness, significant scaling, and possible blistering or pustules. The infection may cause extensive skin damage or thickened, discolored nails.
- Description: The infection has spread significantly, causing more severe symptoms and potentially affecting larger areas or deeper tissues.
Chronic Stage:
- Symptoms: Persistent symptoms that last for months or longer, with frequent flare-ups. The skin may become thickened or cracked, and nails may be severely damaged.
- Description: Long-term, ongoing infection that is difficult to treat and manage. It may require extended treatment and can lead to complications if not addressed effectively.
Resolution:
- Symptoms: Reduced symptoms and healing of affected areas, though some residual symptoms or changes may remain.
- Description: The infection is controlled or eradicated with treatment, but monitoring is essential to prevent recurrence.
Treatment
Topical Antifungals:
- Creams, Ointments, or Powders: Applied directly to the affected area (e.g., clotrimazole, terbinafine).
Oral Antifungals:
- Tablets or Capsules: For more severe or widespread infections (e.g., fluconazole, itraconazole).
Antifungal Shampoos:
- For Scalp Infections: Medicated shampoos to reduce fungal growth (e.g., ketoconazole shampoo).
Good Hygiene Practices:
- Keeping Affected Areas Clean and Dry: Preventing further fungal growth.
- Avoiding Sharing Personal Items: Such as towels or shoes.
Lifestyle Adjustments:
- Wearing Breathable Clothing: To reduce moisture accumulation.
- Changing Socks and Shoes Regularly: To prevent athlete’s foot.
Management of Underlying Conditions:
- Controlling Diabetes or Other Conditions: That can increase susceptibility to fungal infections.
Proper Treatment of Infected Areas:
- Regular Cleaning: Using antifungal soaps or wipes for affected skin.
Avoiding Triggers:
- Avoiding Known Irritants: Such as harsh chemicals or fabrics that can exacerbate symptoms.
What Should You Avoid
- scratching or rubbing.
- sharing personal items.
- wearing damp or tight clothing.
- ignoring hygiene practices.
- using over-the-counter products without consulting a doctor.
- using harsh or fragranced products.
- exposing affected areas to contaminated surfaces.
- discontinuing treatment prematurely.