Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
content of this page
1- Introduction
2- Anatomical Overview
3- Treatment
4- purposes
Introduction
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a medical condition that occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand, becomes compressed at the wrist. The carpal tunnel is a narrow, rigid passageway of ligament and bones at the base of the hand, which houses the median nerve and the tendons that bend the fingers.
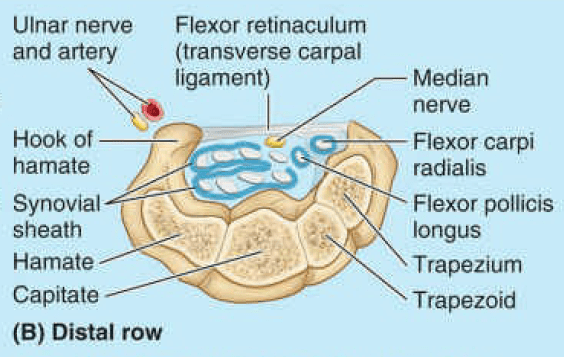
Anatomical Overview
Clinically, the syndrome consists of a burning pain or “pins and needles” along the distribution of the median nerve to the lateral three and a half fingers and weakness of the thenar muscles. It is produced by compression of the median nerve within the tunnel. The exact cause of the compression is difficult to determine, but thickening of the synovial sheaths of the flexor tendons or arthritic changes in the carpal bones are thought to be responsible in many cases.
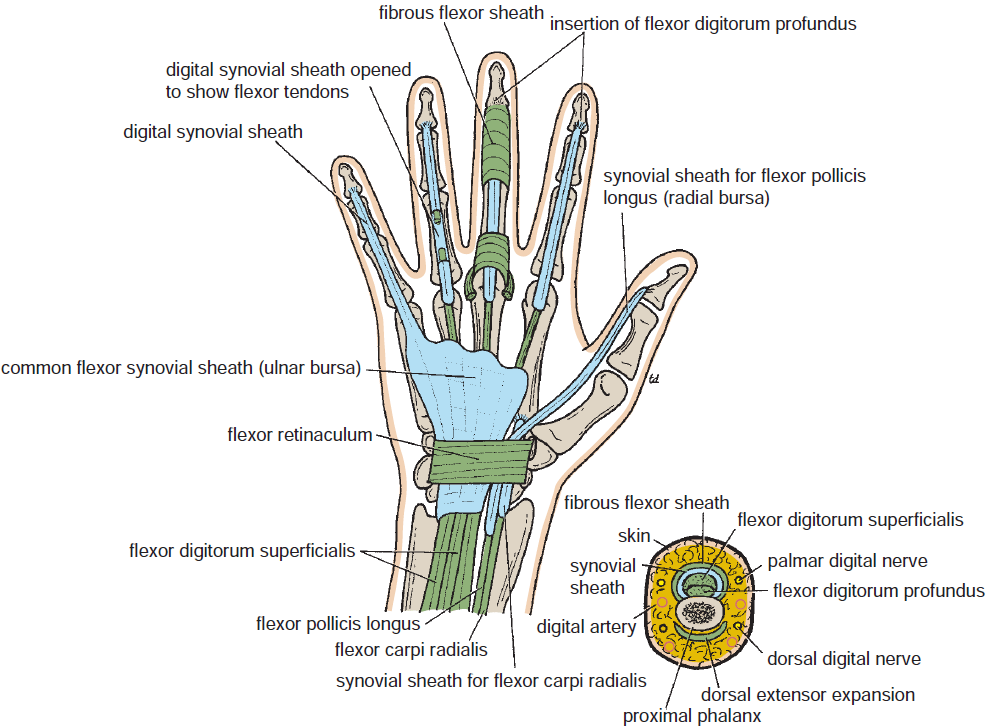
Treatment
partial or complete surgical division of the flexor retinaculum, a procedure called carpal tunnel release, may be necessary. The incision for carpal tunnel release is made toward the medial side of the wrist and flexor retinaculum to avoid possible injury to the recurrent branch of the median nerve.
Purposes
to free The median nerve which provides sensory and motor functions to the thumb and 3 middle fingers which may be lost because of the syndrome.