Trigger Finger
content of this page
1- Introduction
2- Anatomical Overview
3- Treatment
4- purposes
Introduction
It’s a condition that affects the tendons in the fingers or thumb, causing pain, stiffness, and a sensation of locking or catching when you bend and straighten your finger. This happens when the flexor tendons, which control the bending of the fingers, become irritated and swollen, making it difficult for the tendon to glide smoothly through its sheath.
Anatomical Overview
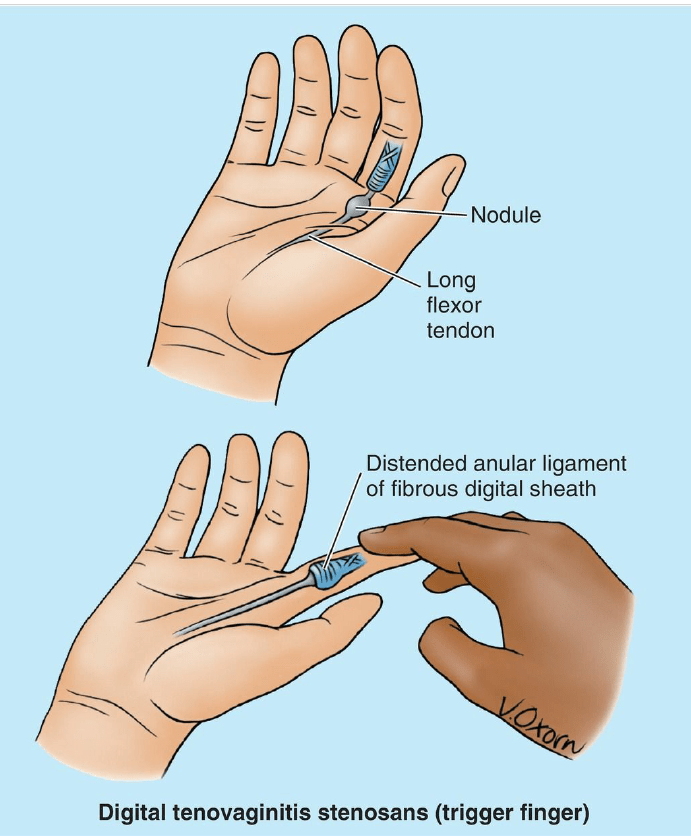
The Thickening of a fibrous digital sheath on the palmar aspect of the digit
produces stenosis of the osseofibrous tunnel, the result of repetitive forceful use
of the fingers. If the tendons of the FDS and FDP enlarge proximal to the
tunnel, the person is unable to extend the finger. When the finger is extended
passively, a snap is audible. Flexion produces another snap as the thickened
tendon moves. This condition is called digital tenovaginitis stenosans (trigger
finger or snapping finger).
Treatment
Rest and Activity Modification: Avoiding activities that exacerbate the condition can help reduce symptoms.
Splinting: Wearing a splint at night to keep the affected finger in an extended position can help rest the tendon.
Medications:
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Medications like ibuprofen or naproxen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Corticosteroid Injections: These can be injected into the tendon sheath to reduce inflammation and swelling, providing relief for several months.
Physical Therapy: Stretching and strengthening exercises can improve the condition.
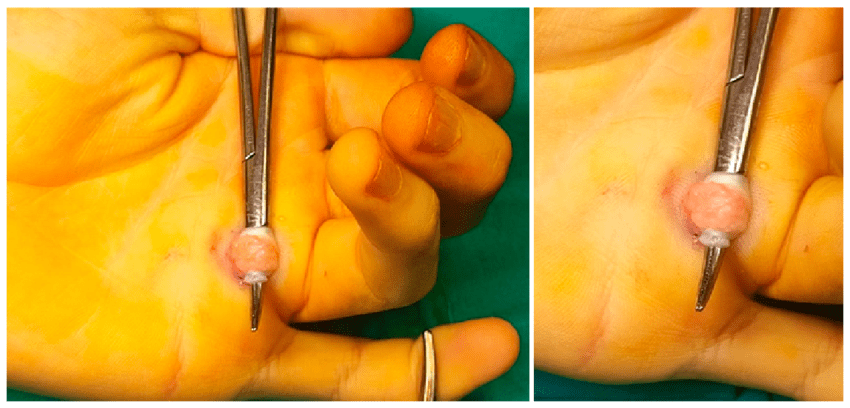
Surgery: If other treatments are not effective, a surgical procedure called “percutaneous release” or “open surgery” may be performed to release the constricted part of the tendon sheath.
Other Therapies: Alternative treatments such as acupuncture or massage may provide relief for some individuals.
Purposes
- Restore Normal Function: Enable the smooth, pain-free movement of the affected finger or thumb.
- Improve Quality of Life: Restore the ability to perform daily activities without discomfort or limitation.