Refractive index of glass, by real and apparent depth using a traveling microscope
Content of this page :
1. Introduction of the experiment.
2. Aim of the experiment.
3. Tools of the experiment.
4. Steps and methods of the experiment.
5. Table of The Readings.
6. Medical application and advantages of the experiment.
1. Introduction of the experiment:
The experiment to determine the refractive index of glass using real and apparent depth with a traveling microscope is a fundamental exercise in optics. It explores the principles of refraction and the behavior of light when it passes through a transparent medium like glass.
2. Aim of the experiment:
-To measure the refractive index of glass.

3-Tools of The experiment
- Traveling microscope
- Slap of glass
- Object like paper that had written with (x).

4. Steps and methods of the experiment:
1. Place the paper that had written (x).
2. Be careful, adjust the cross- hairs of the microscope so that you can be clearly seen without strain.
3. Place the microscope vertically above the object (x) and adjust the height of the instrument until the object (x) is in sharp focus with no parallax between their image and the cross- hair, Read the vertical venire scale of the microscope and record the reading, this reading is (d ).
4. Place the glass vertically above the object (x) and adjust the height of the instrument until the object (x) is in sharp focus with no parallax between their image and the cross- hair, Read the vertical venire scale of the microscope and record the reading, this reading is (d).
5. Place the object (x) above the glass and place the microscope vertically above the object (x) adjust the height of the instrument until the object (x) is in sharp focus with no parallax between their image and the cross- hair, Read the vertical vernire scale of the microscope and record the reading, this reading is (d3).
5. Table of the Readings:
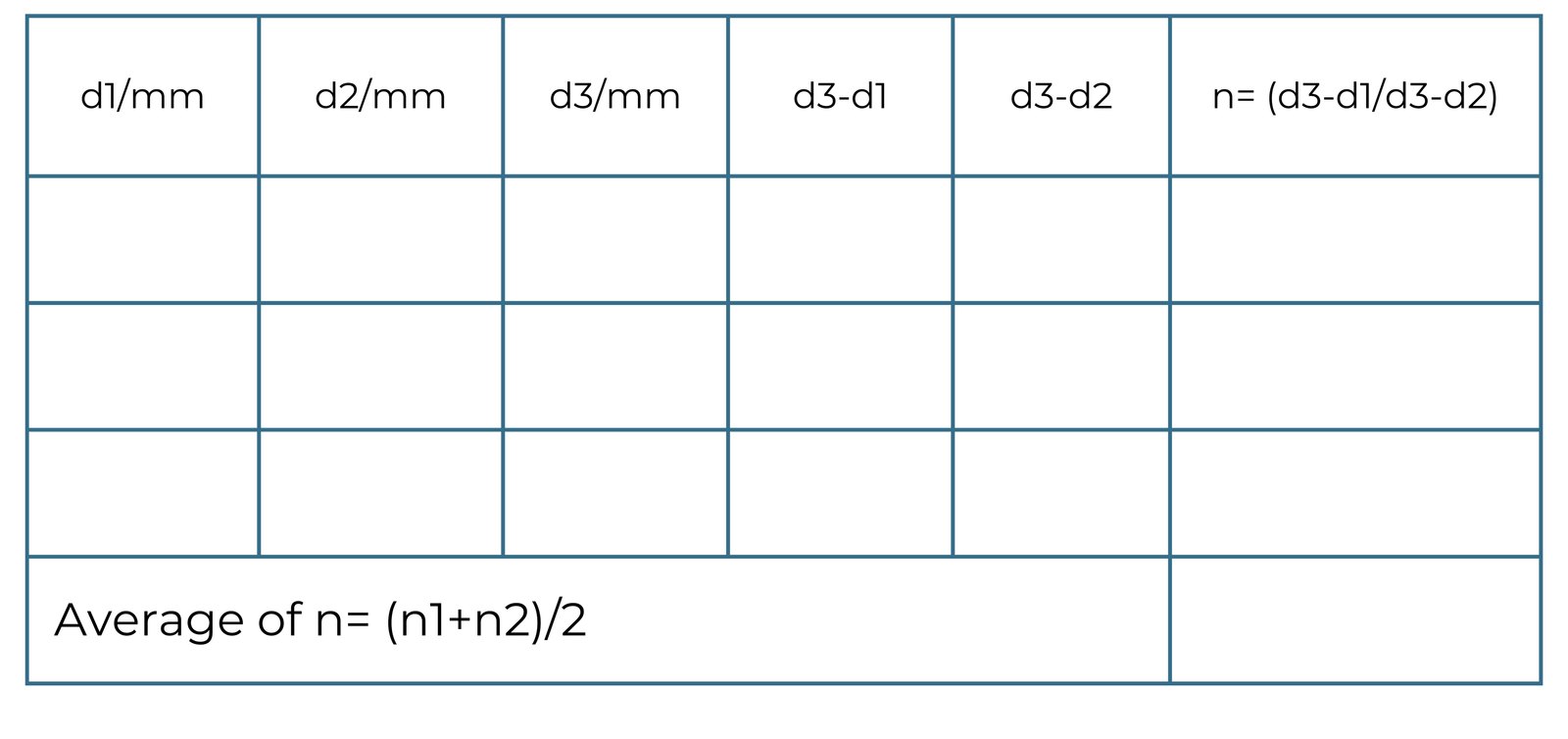
n= 1.52
6-Medical application
Ophthalmic Refractive Surgery:
- Application: In procedures like LASIK (Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis), precise knowledge of the refractive index of corneal tissues is crucial. This knowledge helps in accurately shaping the cornea to correct refractive errors such as myopia, hyperopia, and astigmatism.
- Use of Refractive Index: Understanding how light bends through corneal tissue (similar to glass in the experiment) helps in optimizing laser parameters and predicting post-operative outcomes. The refractive index determination contributes to the accuracy and safety of surgical interventions.
Contact Lens Design:
- Application: Contact lenses are designed to correct vision by focusing light properly onto the retina. The refractive index of lens materials is essential in determining their optical properties.
- Use of Refractive Index: By accurately measuring and understanding the refractive index of lens materials (through similar experimental techniques), manufacturers can optimize lens designs to provide better visual acuity and comfort for patients.
Diagnostic Imaging Techniques:
- Application: Techniques like Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) and confocal microscopy rely on understanding light propagation through tissues and transparent media.
- Use of Refractive Index: Knowledge of refractive indices aids in calibrating imaging systems and interpreting images accurately. For instance, in OCT, knowing the refractive index of tissue structures helps in precise depth profiling and imaging resolution enhancement.
Biomedical Optics and Spectroscopy:
- Application: Spectroscopic techniques (e.g., Raman spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy) are used for biochemical analysis and disease detection.
- Use of Refractive Index: Understanding how light interacts with biological samples (similar to how it interacts with glass in the experiment) helps in designing and interpreting optical systems for medical diagnostics. Accurate refractive index data contributes to the sensitivity and specificity of spectroscopic analyses.
Microsurgery and Minimally Invasive Procedures:
- Application: During delicate surgeries and procedures where precision is paramount, such as neurosurgery or endoscopic interventions.
- Use of Refractive Index: Knowledge of refractive indices aids in designing and using optical fibers, lenses, and endoscopes to visualize and manipulate tissues accurately. This ensures minimal tissue damage and precise targeting of treatment areas.
